Ngorongoro Crater, a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in northern Tanzania, is a geological marvel and a prime wildlife destination. Known for its unique landscape and diverse ecosystems, the crater holds several notable records that highlight its significance in the world of natural wonders and conservation. Here’s a detailed look at the remarkable records associated with Ngorongoro Crater.
Largest Unbroken Caldera
- Geological Significance
Ngorongoro Crater is renowned as the largest unbroken caldera in the world. Formed millions of years ago by a volcanic eruption, the crater’s size and shape make it a unique geological feature.
- Dimensions: The crater measures approximately 19 kilometers (12 miles) in diameter and is around 610 meters (2,000 feet) deep. Its expansive floor covers about 260 square kilometers (100 square miles), providing a vast and diverse habitat for wildlife.
- Volcanic History: The crater’s formation is the result of a volcanic explosion followed by the collapse of the volcano’s cone. This geological process has created a distinctive landscape characterized by its steep walls and flat floor.
Highest Density of Wildlife in Africa
- Wildlife Population
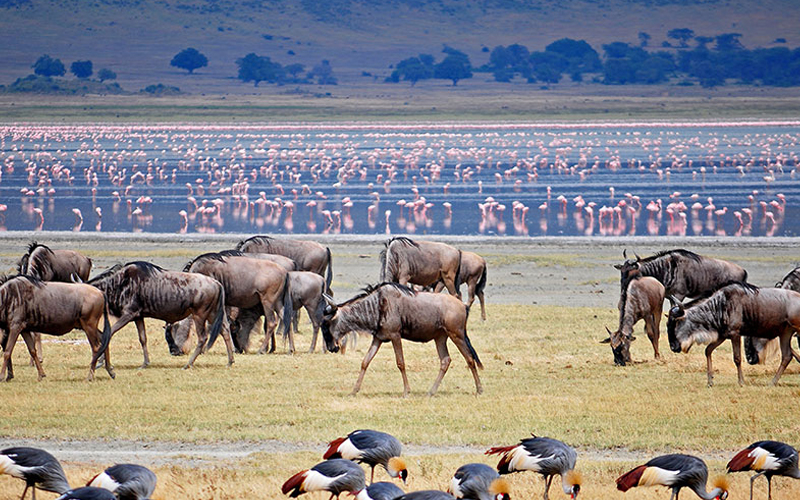
Ngorongoro Crater is famous for its incredible concentration of wildlife. It boasts one of the highest densities of large mammals in Africa, including lions, elephants, and wildebeests.
- Big Five: The crater is home to the Big Five: lions, leopards, elephants, buffaloes, and rhinoceroses. This high concentration of species makes it a top destination for wildlife enthusiasts and photographers.
- Unique Ecosystem: The diverse habitats within the crater, including grasslands, swamps, and forests, support a rich variety of wildlife. The relatively small size of the crater ensures that animals are more easily spotted compared to other regions.
Largest Population of Black Rhinoceroses
- Rhino Conservation
Ngorongoro Crater is renowned for having one of the largest populations of black rhinoceroses in Tanzania. These critically endangered animals find refuge in the crater’s protected environment.
- Conservation Efforts: Conservation programs and anti-poaching measures have been implemented to protect the black rhinos. These efforts have contributed to the stabilization and growth of the rhino population within the crater.
- Viewing Opportunities: Visitors to Ngorongoro Crater have a high chance of spotting black rhinoceroses, thanks to the focused conservation efforts and the relatively small size of the crater.
Richest Birdlife in a Single Area
- Bird Species Diversity
The crater’s diverse habitats support a high variety of bird species, making it one of the richest birding destinations in Africa. Over 500 bird species have been recorded in the area.
- Notable Species: Birdwatchers can observe species such as the Kori Bustard, the Secretary Bird, and various types of vultures and eagles. The crater’s unique landscape provides ideal conditions for a wide range of avian species.
- Migratory Birds: Ngorongoro Crater also serves as a crucial stopover for migratory birds, adding to its significance as a birdwatching destination.
Highest Number of Endangered Species
- Endangered Wildlife
In addition to black rhinoceroses, Ngorongoro Crater is home to several other endangered species, including the endangered Ethiopian wolf and rare bird species.
- Conservation Successes: The crater’s status as a protected area has played a significant role in the conservation of these endangered species. Ongoing efforts aim to maintain and enhance these populations.
- Research and Monitoring: Scientific research and monitoring programs are essential for understanding the needs of these endangered species and ensuring their continued protection within the crater.
Largest Permanent Water Source
- Water Availability
The crater’s floor features several permanent water sources, including lakes and wetlands, which provide essential resources for the resident wildlife.
- Lake Magadi: Lake Magadi, a saline lake located in the southern part of the crater, is a prominent feature. It supports a variety of bird species, including flamingos, and contributes to the overall ecosystem of the crater.
- Seasonal Variations: The availability of water varies with the seasons, affecting the distribution and behavior of wildlife within the crater. However, the presence of permanent water sources ensures a stable environment for many species.
Highest Concentration of Predators
- Predator Population
Ngorongoro Crater has one of the highest concentrations of predators in Africa, including lions, hyenas, and leopards.
- Predator-Prey Dynamics: The abundance of prey species in the crater supports a robust predator population. This dynamic creates a fascinating ecosystem where predator-prey interactions are readily observable.
- Research and Observation: Ongoing research in the crater helps in understanding predator behavior and interactions, contributing to broader conservation and ecological knowledge.
Oldest and Most Stable Ecosystem
- Ecosystem Stability
Ngorongoro Crater’s ecosystem is one of the oldest and most stable in Africa, thanks to its isolated environment and protected status.
- Ecological Balance: The crater’s stable climate and consistent resources support a balanced and resilient ecosystem. This stability contributes to the high density of wildlife and the overall health of the environment.
- Historical Significance: The long history of the crater as a protected area has allowed for the development of a unique and stable ecosystem, making it a valuable site for ecological research and conservation.
Most Accessible Wildlife Viewing Area
- Ease of Access
Ngorongoro Crater’s relatively small size and well-maintained roads make it one of the most accessible wildlife viewing areas in Africa.
- Visitor Experience: The ease of access allows visitors to experience a wide range of wildlife and landscapes within a short time. Guided tours and game drives offer opportunities for close encounters with wildlife.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The crater is well-equipped with visitor facilities, including lodges and campsites, which enhance the overall experience and ensure comfort during wildlife viewing.
UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Global Recognition
Ngorongoro Crater is designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site due to its outstanding universal value. This recognition highlights its importance as a natural and cultural treasure.
- Conservation Support: The UNESCO designation helps secure international support for conservation efforts and emphasizes the need to protect the crater’s unique environment and wildlife.
- Educational Value: The crater’s status as a World Heritage Site also serves an educational purpose, raising awareness about the importance of preserving natural wonders and biodiversity.
Ngorongoro Crater stands out as a geological marvel and a haven for wildlife, holding numerous records that underscore its significance. From being the largest unbroken caldera to hosting the highest densities of predators and endangered species, the crater is a remarkable destination for nature enthusiasts and conservationists. Its unique landscape, rich biodiversity, and global recognition make it a crucial site for understanding and preserving our natural heritage.
FAQs
What is the best time to visit Ngorongoro Crater?
The best time to visit Ngorongoro Crater is during the dry season from June to October. This period offers optimal wildlife viewing conditions and pleasant weather.
How can I see the Big Five in Ngorongoro Crater?
Ngorongoro Crater is renowned for its high concentration of the Big Five. To maximize your chances of seeing them, join a guided game drive with a reputable tour operator who knows the best spots and times for wildlife viewing.
Are there any specific conservation programs in place for Ngorongoro Crater?
Yes, several conservation programs focus on protecting the wildlife and habitats within Ngorongoro Crater. These include anti-poaching measures, habitat management, and research initiatives.
What types of accommodations are available near Ngorongoro Crater?
Accommodations near Ngorongoro Crater range from luxury lodges and tented camps to more budget-friendly options. Many lodges offer stunning views and easy access to the crater for game drives.
Can visitors access the crater floor directly?
Yes, visitors can access the crater floor via guided game drives. The roads are well-maintained, and local guides are familiar with the best routes for wildlife viewing.
For an extraordinary Tanzanian adventure, explore the following highlights on our site:
- Zanzibar Beach Tours
- Tanzania Safari
- Ngorongoro Crater
- Kilimanjaro National Park
- Mikumi National Park
- Tarangire National Park
- Lake Manyara National Park
- Arusha National Park
Visit our page for detailed information and tips to plan your perfect Tanzanian journey.






Leave A Comment